Next: Coupled Dimensions of Vibration Up: String Modeling Previous: Commuted Waveguide Synthesis
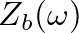 .
.
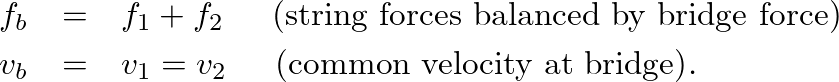
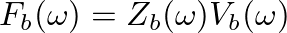 .
.
![\begin{eqnarray*}
Z_{b}(\omega) V_{b}(\omega) &=& F_{b}(\omega) = F_{1}(\omega) ...
...\omega) - \left[V_{b}(\omega) - V_{2}^{+}(\omega)\right]\right\}
\end{eqnarray*}](img40.png)
![$\displaystyle V_{b}(\omega) = H_{b}(\omega) \left[ R_{1} V_{1}^{+}(\omega) + R_{2} V_{2}^{+}(\omega) \right]
$](img41.png)
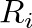 is the impedance of string
is the impedance of string 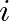 and
and
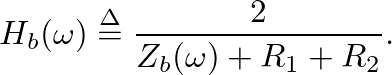
![$H_{b}(\omega) = 2 / \left[Z_{b}(\omega) + R_{1} + R_{2}\right]$](img45.png) to obtain the velocity of the bridge.
to obtain the velocity of the bridge.
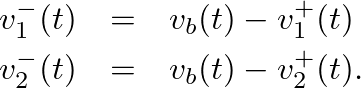
 coupled strings without much difficulty.
coupled strings without much difficulty.

| ©2004-2024 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |