Next: Hooke's Law for Plane Waves Up: Acoustic Systems Previous: Acoustic Impedance
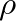 and cross-sectional area
and cross-sectional area 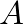 , the section mass is given by
, the section mass is given by 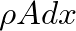 .
.
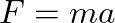 ), we then have:
), we then have:
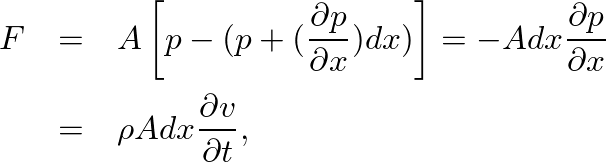
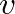 is particle velocity.
is particle velocity.
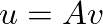 ), we find:
), we find:
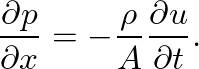 (2)
(2)

| ©2004-2024 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |