Towards Real-Time Single-Channel Speech Separation in Noisy and Reverberant Environments
Julian Neri and Sebastian Braun
This paper is published in the proceedings of the IEEE ICASSP 2023. The oral presentation slides are included below.
Microsoft has a site for this paper here.
Abstract
This website includes audio excerpts that demonstrate our proposed real-time single-channel speech separation models.
All the proposed models are causal and resource-efficient, with the capacity to separate noisy and reverberant speech mixtures in real-time. There are several versions which are evaluated and compared in the paper: an end-to-end version, a cascaded modules version, and a cascaded version that uses subtractive separation.
For comparison, we also provide the results from a state-of-the-art baseline, SepFormer, a large transformer-basedspeech separation model that operates offline (not real-time capable).
A difference between the audio output from offline and real-time models is that the real-time models have an audible initial convergence that is related to the response time of the temporal model. This is a consequence of their causality. They start from a zero-valued initial state and integrate information as time progresses, without having access to future inputs. In contrast, offline methods have the luxury of using both past and future inputs.
When available, the ground-truth source signals are also given. This is not the case for blind datasets of real speech mixtures recorded with a single microphone in a real room environment where two people are simultaneously talking (DNS2022 and REALM).
Audio Examples
DNS2022 – real single-channel speech mixture
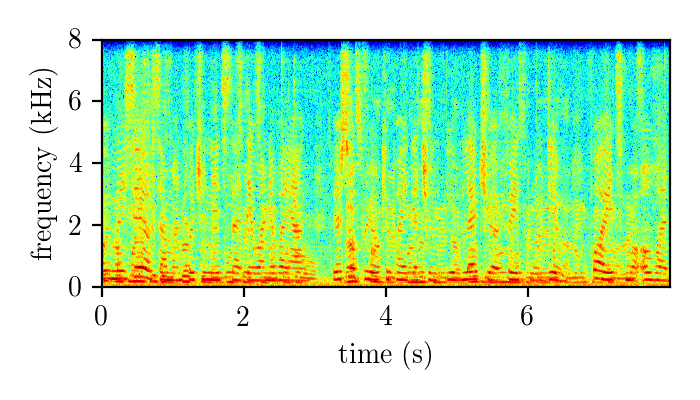
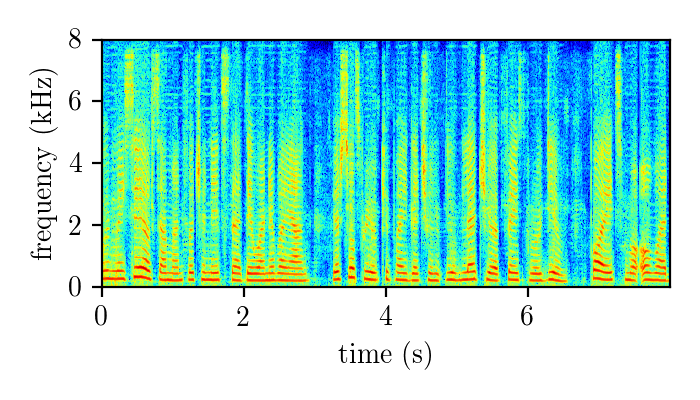
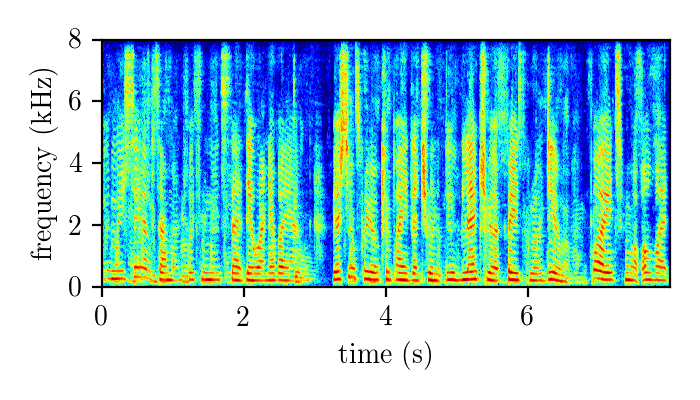
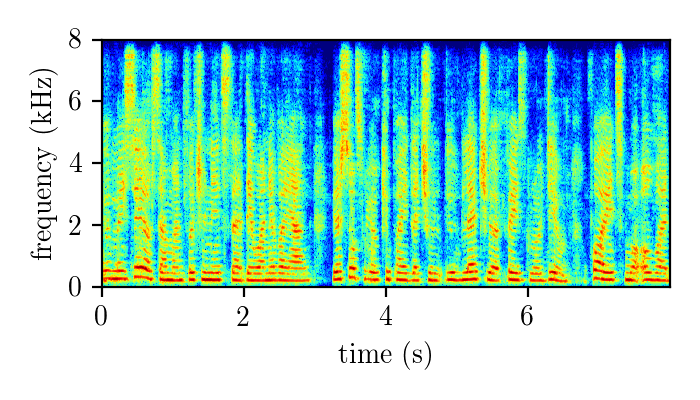
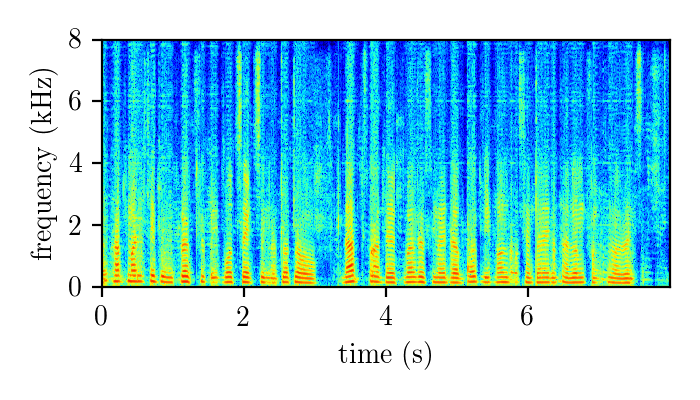
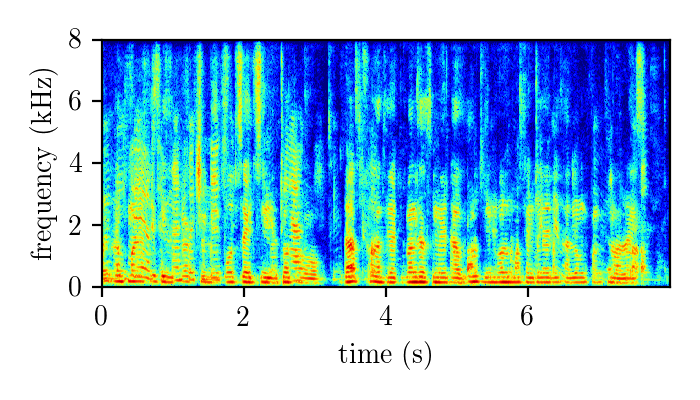
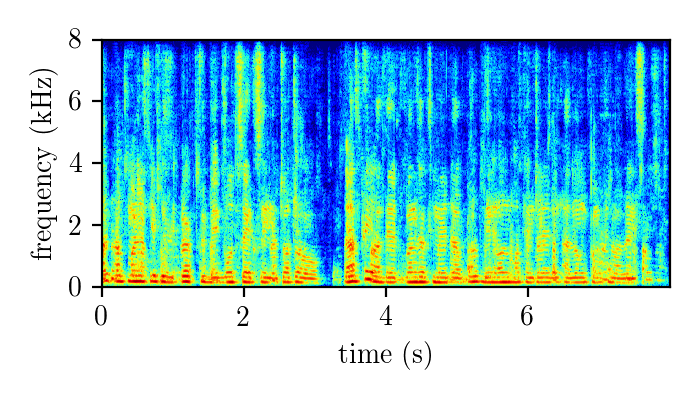
REALM – real single-channel speech mixture
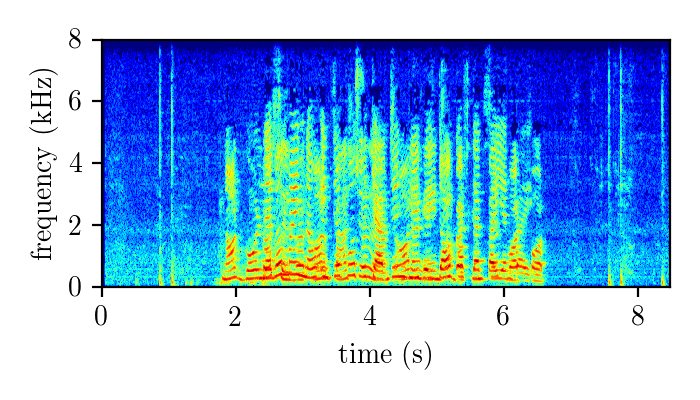
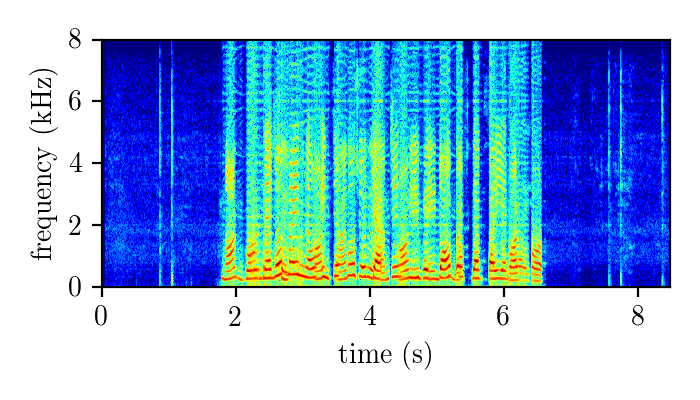
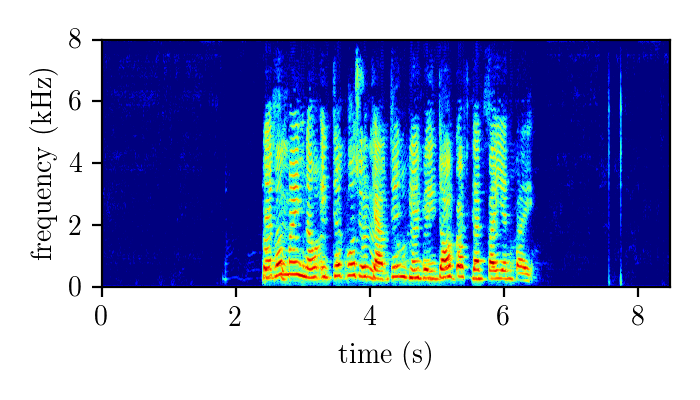
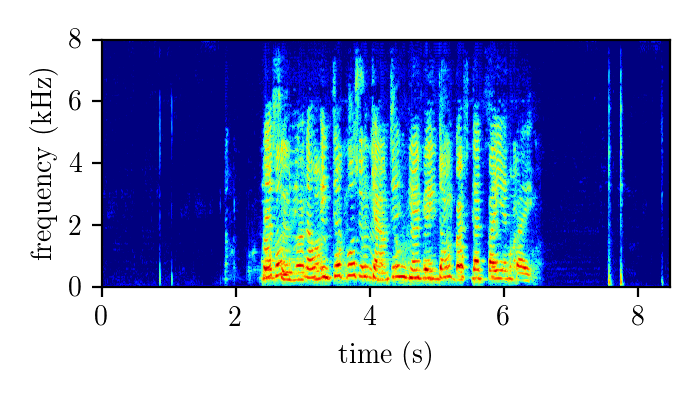
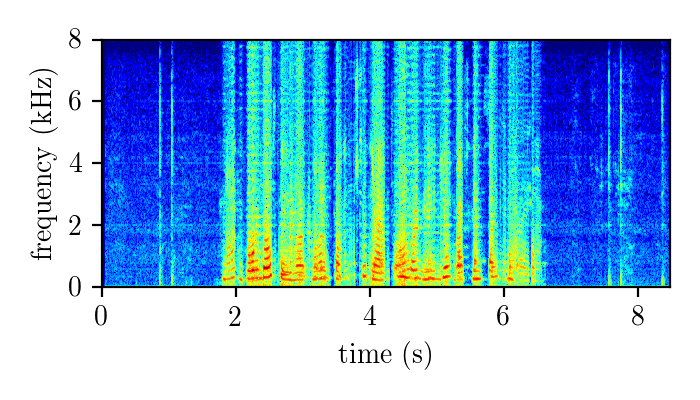
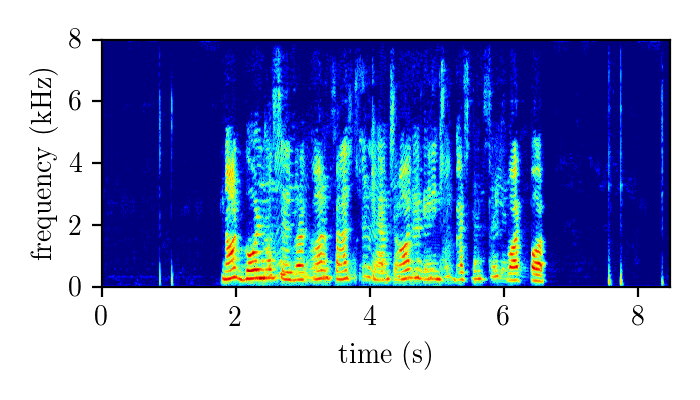
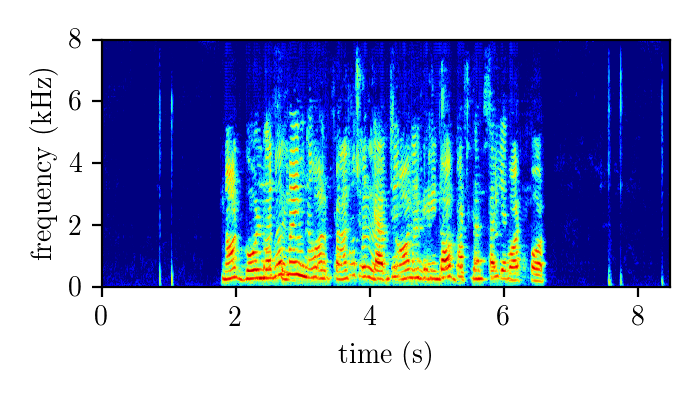
WHAMR – synthetically mixed speech
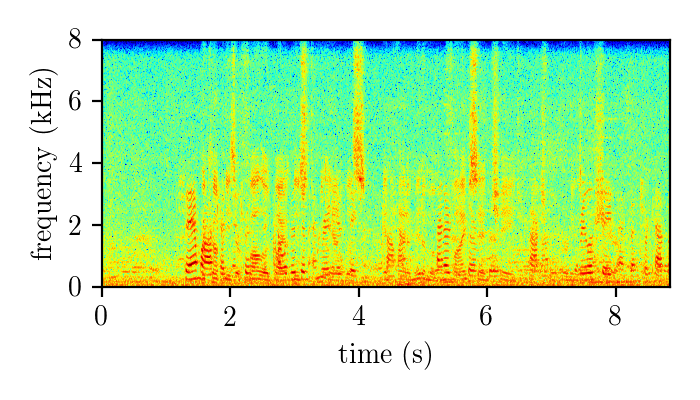
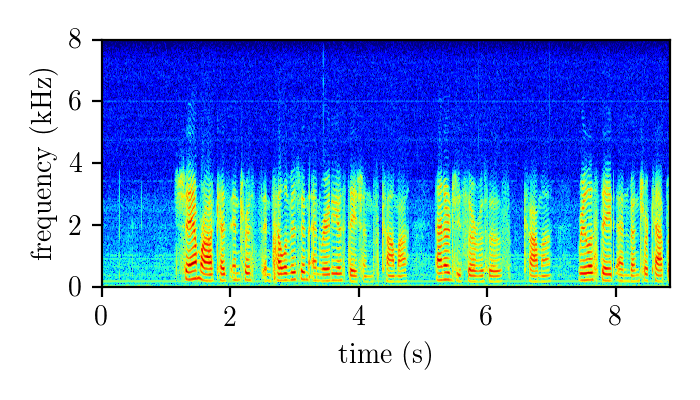
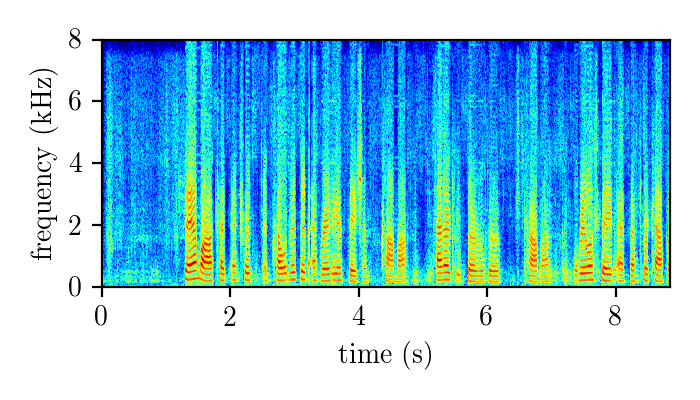
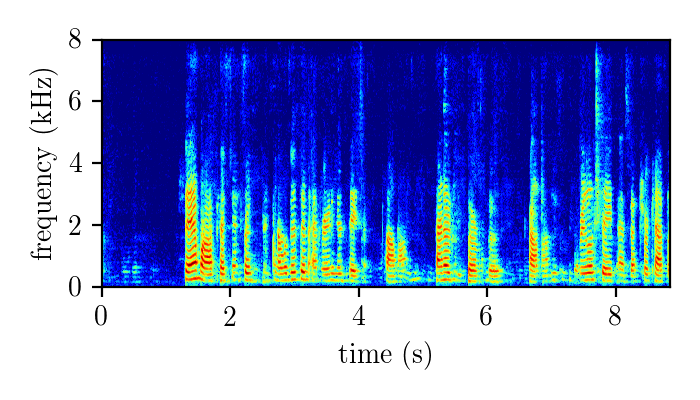
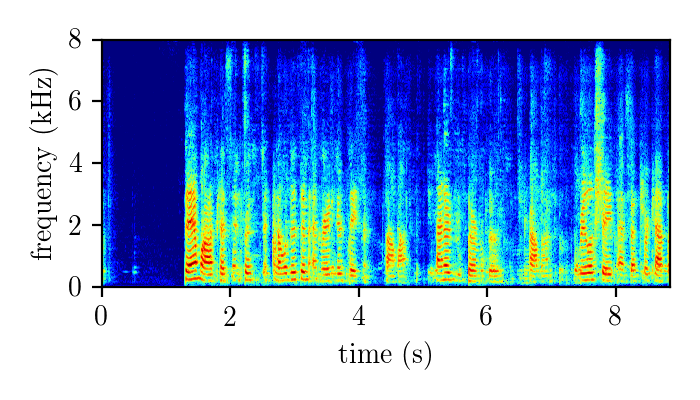
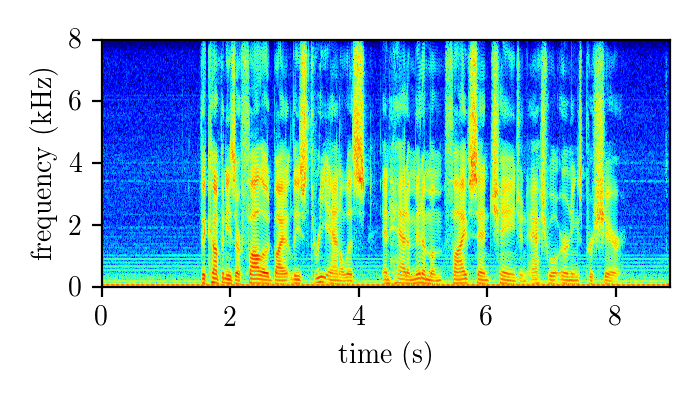
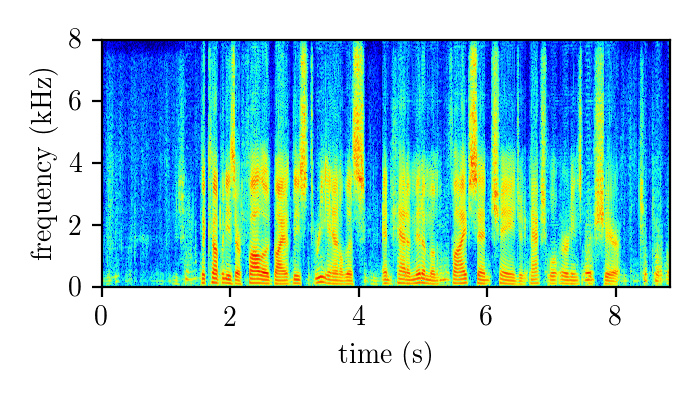
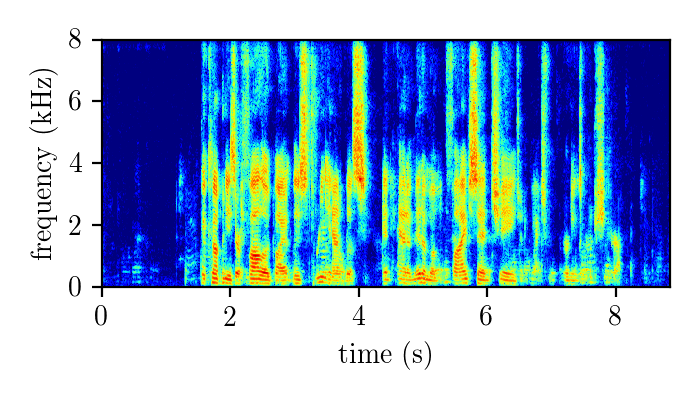
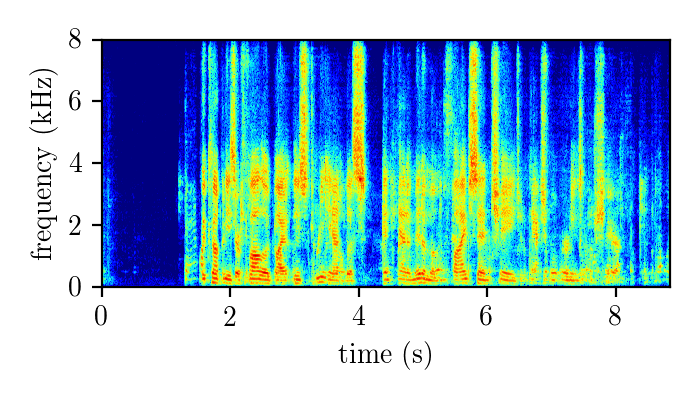
Dereverberation module demonstration
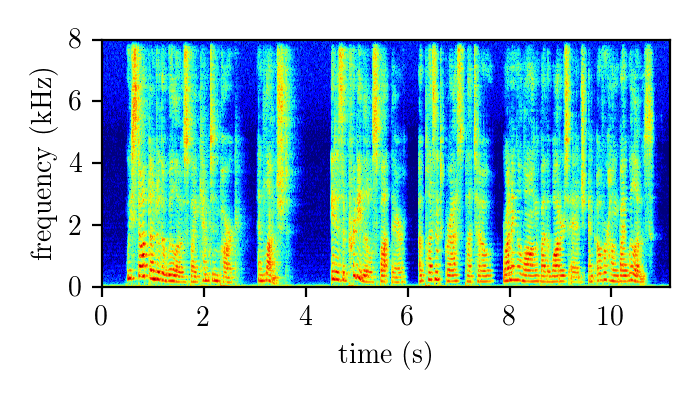
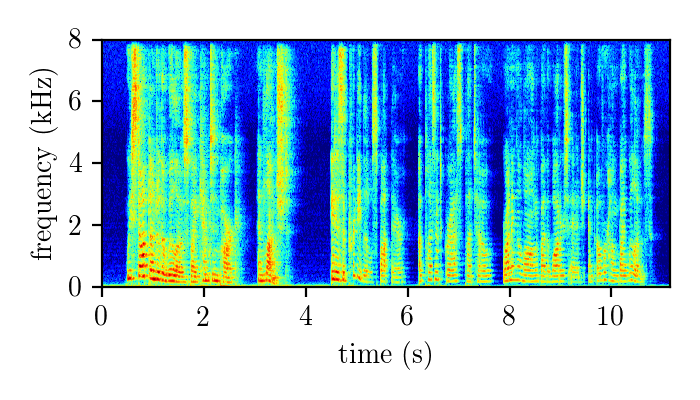
Models
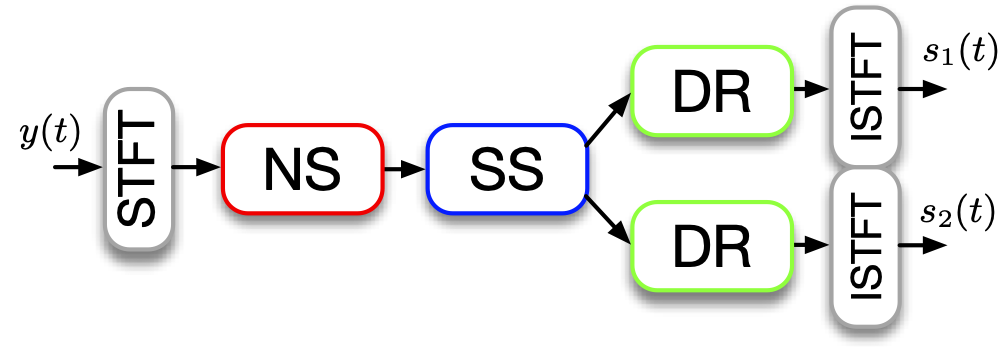
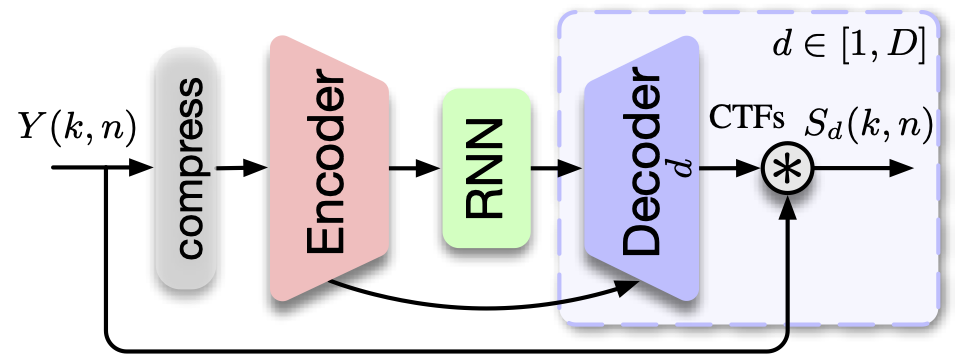
Citation
J. Neri and S. Braun, “Towards real-time speech separation in noisy and reverberant environments”, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) , Rhodes, Greece, June 2023.
BibTex
@inproceedings{Neri:2023:Real:Time:Speech:Separation,
author = {Julian Neri and Sebastian Braun},
title = {Towards Real-Time Speech Separation in Noisy and Reverberant Environments},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
year = {2023},
pages = {1-5},
month = {June},
address = {Rhodes, Greece},}